The Origin of Zero: How 'Nothing' Became Everything in Math
What is the answer for 4-4, or 5 x 0? Yes, you are correct; the answer is 0. 0 is the basis of the binary system; it is a key factor in driving today’s digital progress. But have you ever pondered on the value of ‘0’? When you look at it, it can be nothing or the most important number in mathematics. We cannot imagine life today without the number ‘0,’ but yet there was a time when 0 didn’t exist. The numbers started from 1, so how did 0 come into existence? Like many interesting concepts, 0 also has its own story and history. And in our endeavor to make math easier and interesting at Askmathguru, we like to share some interesting tidbits about math and mathematical concepts that will make you a bit more interested in math. One such story is about the origin of 0. So, let's dive deep into the pages of history to learn how 0 originated and how it became an indispensable part of the world.
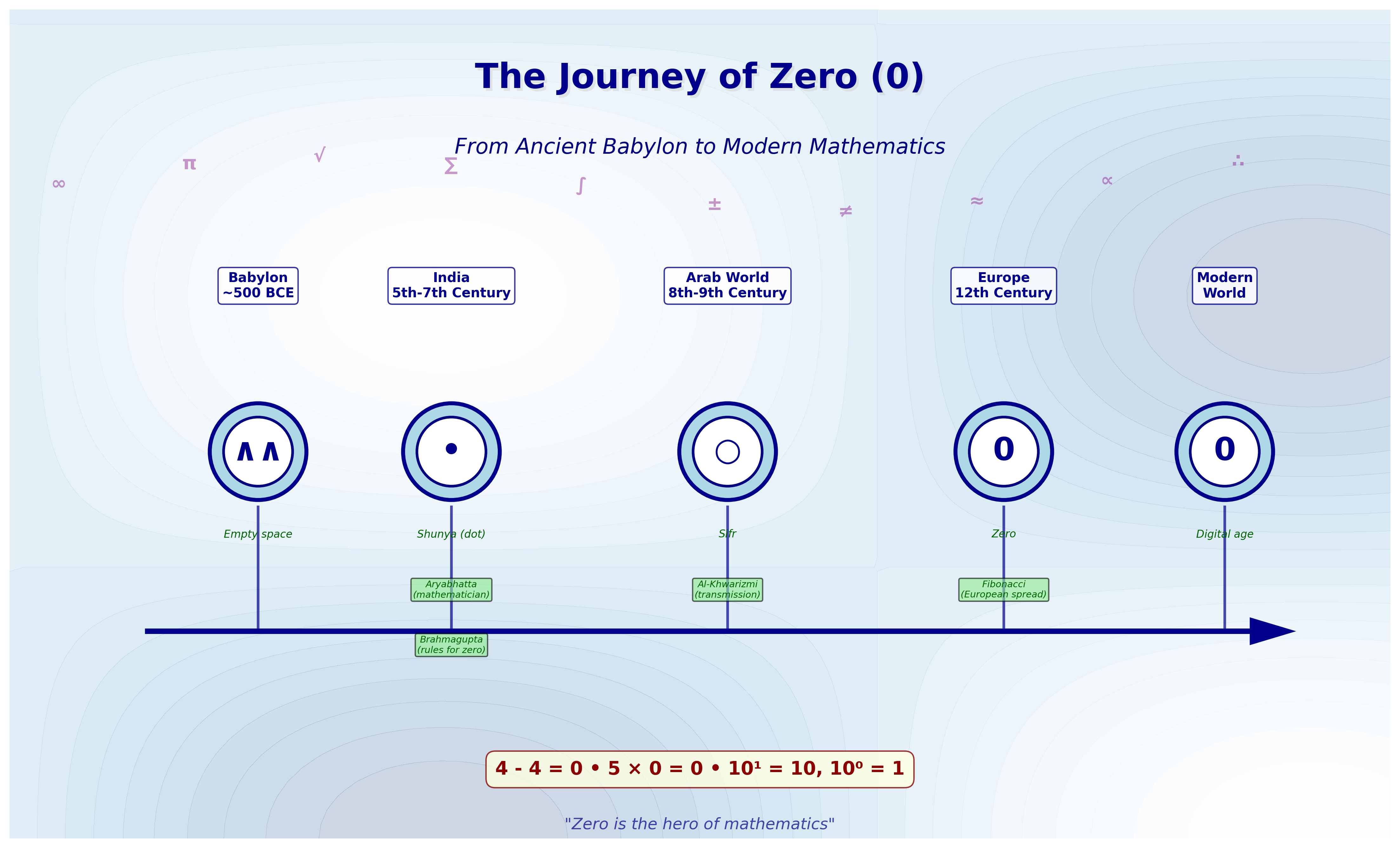
It is a widely known fact that the credit for the invention of zero goes to India. And although India did invent the actual ‘0’ as we know it, there were a few earlier attempts by ancient civilizations to use something that resembled zero. The earliest known use of a semblance of zero was in Babylon. They used a certain special symbol in place of “none” or zero. For instance, they used a symbol to distinguish 101 from 11. However, it was not a proper number. Then the real deal-breaker came in ancient India.
Around the 5th to 7th centuries, an Indian mathematician, Aryabhatta, was the first to define the actual zero. He defined the value of zero in the decimal system. And the number was called “shunya,” which means

“empty” or “void.” The ancient zero was represented as a small dot under numbers. Aryabhatta’s work was later developed by Brahmagupta, who defined the use of zero in arithmetic calculations.
The transmission of the zero concepts from India to Europe was expedited by the Latin translation of al-Khwarizmī’s seminal work, Algoritmo de Numero Indorum, in the 12th century. This translation served as a pivotal conduit, connecting the mathematical legacies of ancient India with the Arab world and, subsequently, with Europe.
Zero gradually travelled to the Western world through Arab mathematicians. The Indian numerals, including zero, were adopted by the Islamic world. Arab mathematicians introduced the zero to the Arab world, and from there it travelled to Europe. One noteworthy contribution to this transmission was the work of al-Khwarizmī, an Arab mathematician. The Latin translation of his seminal work, Algoritmo de Numero Indorum, in the 12th century, proved to be a pivotal conduit connecting the mathematical concepts of ancient India to Europe via the Arab world.
However, it was not an easy journey. Medieval European mathematicians were skeptical of the concept of “nothing.” However, they later caught on to the concept thanks to Fibonacci. Fibonacci learned about the concept of zero from Arab traders when he was travelling with his father. He immediately recognized the power of the Arab decimal system over the then-existing Roman numerals. He published the concept of zero in his work, and the concept of zero was spread to the Western world.
Once the system of zero was established, there was no looking back. It revolutionized the concept of accounting, engineering, and science. It entered the part and parcel of daily life. And now, we can't imagine life without zero. Without zero, there would be no calculus, binary system, or modern technology. Although it may represent nothing, its value has everything. No wonder it is called the silent hero of mathematics. Even though its value might mean nothing, zero has the power to change the world. So let's pay respect to this silent hero the next time we see zero.