From Triangles to Technology: The Power of Pythagoras’ Theorem
There are several mathematical principles that are used in real-life applications that we aren’t even aware of. One such widely used principle is the Pythagorean theorem. We all know that the Pythagorean theorem is related to right-angled triangles, but few of us are aware that it is frequently used in the construction industry or in face recognition systems in security cameras. Askmathguru has embarked on a journey to make math easier and simpler, and one such venture is to make math interesting by sharing fun facts about math. So, let's dive in and learn a bit more about the Pythagorean theorem.
As you have rightly guessed, the Pythagorean theorem is about the lengths of sides of a right-angled triangle. The scientific wording of the theorem is “the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides,” or in simpler terms, “the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the lengths of the other two sides of a right-angled triangle.” It can be written as
Where, a and b are the sides of the right angle in a right-angled triangle and c is the hypotenuse or the side opposite to the right angle.
For instance, suppose ΔABC is a right-angled triangle with sides AB = a = 3 cm, BC = b = 4 cm, and the length of side AC is unknown. Then by applying the Pythagorean theorem,
Using the Pythagorean theorem, finding lengths of sides of a right-angled triangle becomes as simple as pie. Now let’s expand our knowledge by learning a few interesting facts about the theorem. Most of us are under the impression that the Pythagorean theorem was developed by Pythagoras, and it is true that Pythagoras developed the theory around 570 BCE, but actually the theory had been around for a while before that. The credit for the oldest known records for the theory goes to Babylonians. There is evidence of Babylonians using triplets satisfying the theorem as early as 1800 BCE. However, they used it for practical problems in construction instead of as a mathematical formula. Similarly, such evidence was found in the Rhind Mathematical Papyrus around 1650 BCE, which proved that the ancient Egyptians had the knowledge about geometric principles and they used them for the construction of pyramids. Additionally, there is similar evidence that some form of this theorem was known in the ancient Indian and Chinese cultures.

Later, around 500 BCE, Pythagoras of Samos, a Greek mathematician and philosopher, formally introduced this theorem. Though it is unknown whether he actually provided formal proof of the theorem, he is usually credited with the theorem. This theorem was then translated by the Islamic mathematicians during the Islamic Golden Age, when they translated and preserved works of Greek mathematicians. Thus, the theorem became widely known and then used as a founding block for various algebraic and geometric principles.
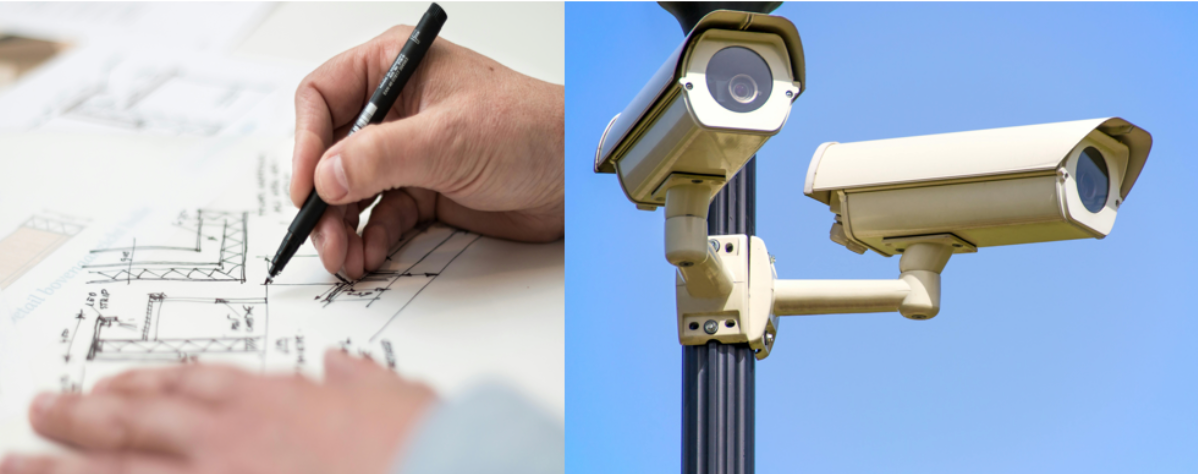

The Pythagorean theorem is widely used now and is the foundation of geometry, trigonometry, algebra, physics, engineering, and digital technologies. It is one of the basic principles of mathematics and is often taught at an early stage to build the understanding of further principles for the students. With its practical applications and use since ancient times, no wonder it is one of the most famous and well-known mathematical principles of all time. Indeed, it is a testament to the universality of mathematical thought.


